
The significance of Journal Impact Factors (JIF) in academic research lies in their ability to impact financing and career decisions and their frequent use in evaluating the caliber and significance of the study. Impact factoring has drawn criticism for its shortcomings and possible biases, though.

This blog aims to investigate the intricacies of JIFs, scrutinize their benefits and drawbacks, and thoroughly comprehend their function in scholarly investigations.
What is a Journal Impact Factor?
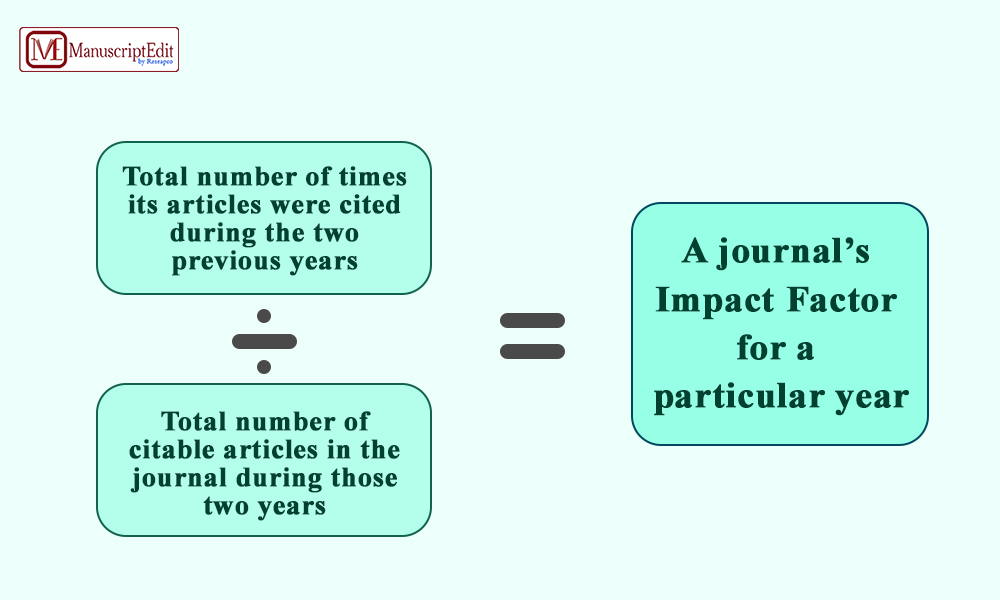
An academic journal’s impact in its field is gauged by its Journal Impact Factor. Impact factor check is done by dividing the total number of articles published in a certain period by the number of citations to articles published in the journal.
Impact factor formula = Number of citations in year X / Number of articles published in years X-1 and X-2
An example of a multidisciplinary scientific journal with a high impact factor is “Nature,” which is regularly cited and significantly influences the scientific community.
How do you Analyze the Impact Factor of a Journal?
To assess a journal’s impact factor, I would consider the following:
- Determine the impact factor by counting the citations that papers published in the journal over the preceding two years obtained.
- Examine the impact factor of other publications within the same field.
- Examine the journal’s editorial board, publishing policies, and article caliber.
- Evaluate the journal’s pertinence to your field of study.
- Consider other metrics such as Altmetrics, Source-Normalized Impact per Paper, and SCImago Journal Rank.
 What Impact Factor is considered good for a Journal?
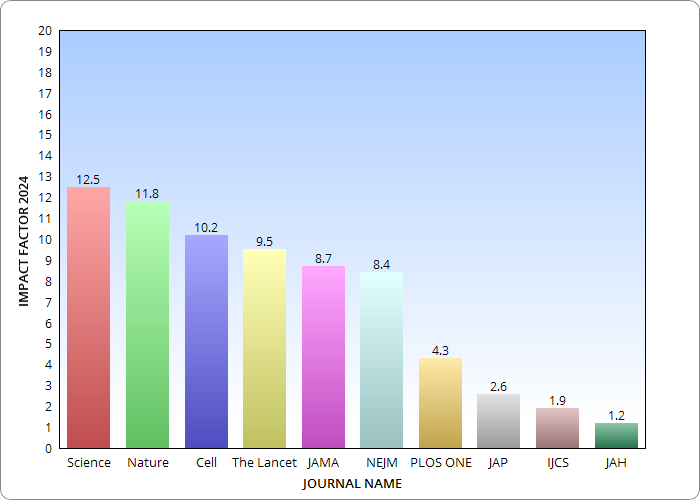
What Impact Factor is considered good for a Journal?A research journal impact factor of 10 or higher is considered excellent, while three is considered good. However, it’s important to note that the impact factor is only meaningful when comparing journals within the same discipline. Some impact factor journals list are Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, Chemical Reviews, and Nature Reviews Drug Discovery.
- Short citation window, which only covers a small portion of citations collected over time
- Inflate citation counts owing to front matter inclusion
- Calculations skewed by a few highly cited publications
- Inappropriate use in cross-field comparisons
- Inflation overall brought on by a rise in academic publications and references per work.
Why are Journal Impact Factors problematic?
The journal impact factors are problematic for multiple reasons.
Advantages and Limitations of Journal Impact Factors
- Alternative metrics encompass article-level metrics (e.g., citations, downloads) and altmetrics (e.g., social media mentions).
- Journal-level metrics such as SCImago Journal Rank and Source-Normalized Impact per Paper are also relevant.
- Future directions include a stronger focus on open access and open science initiatives.
- The development of more comprehensive and nuanced metrics is anticipated.
- Evaluation of research will change dramatically with the integration of AI and ML.
Conclusion
To sum up, exploring the intricacies of journal impact variables highlights the diverse aspects of scholarly influence evaluation. It is crucial to comprehend their subtleties, constraints, and substitute measurements to make well-informed decisions on academic publishing.
By accepting this knowledge, researchers can move more confidently and clearly through the educational landscape.
References
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/impact-factors-journal-rankings-understanding-metrics/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4150161/
